When depressed, anxious, or going through a period of extended stress, your doctor may prescribe Lexapro as a treatment. The medication is designed to help regulate serotonin levels in the brain, which can help ease symptoms of depression and anxiety.
But, like all medications, Lexapro can also carry a risk for certain side effects. Knowing what to watch out for is important when taking this medication. In this article, we’ll discuss the most common side effects of Lexapro.
Lexapro (escitalopram) is a medication used to reduce anxiety and improve symptoms of depression. It belongs to a class of drugs called Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) that work by increasing serotonin in the brain. Stable serotonin levels can improve sleep, memory, appetite, mood and anxiety.
Lexapro is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder. Below are symptoms that occur with those diagnoses:
Lexapro can also be used off-label (not approved by the FDA) for other mental health diagnoses including obsessive-compulsive disorder, post traumatic stress disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder and some eating disorders.
There are certain populations that require close monitoring or adjustments when using this medication. For children, teenagers and young adults, antidepressant medications like Lexapro can lead to increased suicidal thoughts and therefore these age groups should be monitored closely if receiving this medication. For individuals who have been diagnosed with bipolar disorder, Lexapro and other antidepressant medications should be avoided or require a concomitant mood stabilizing medication. Individuals with heart, kidney, liver or seizure issues may require close monitoring or dosage adjustments. People who are pregnant or breastfeeding should speak with a provider about risks for transmitting Lexapro to the infant and whether it is safer to treat symptoms with or without the medication. Finally, older adults taking Lexapro require reduced dosing to prevent excessive or dangerous side effects.
Lexapro is a safe and effective option for treating depression and anxiety. However, using this medication isn’t risk-free, and risks/benefits should be discussed with a prescribing provider before initiating treatment. It should also be noted which side effects are most likely to occur and if they will dissipate over time.
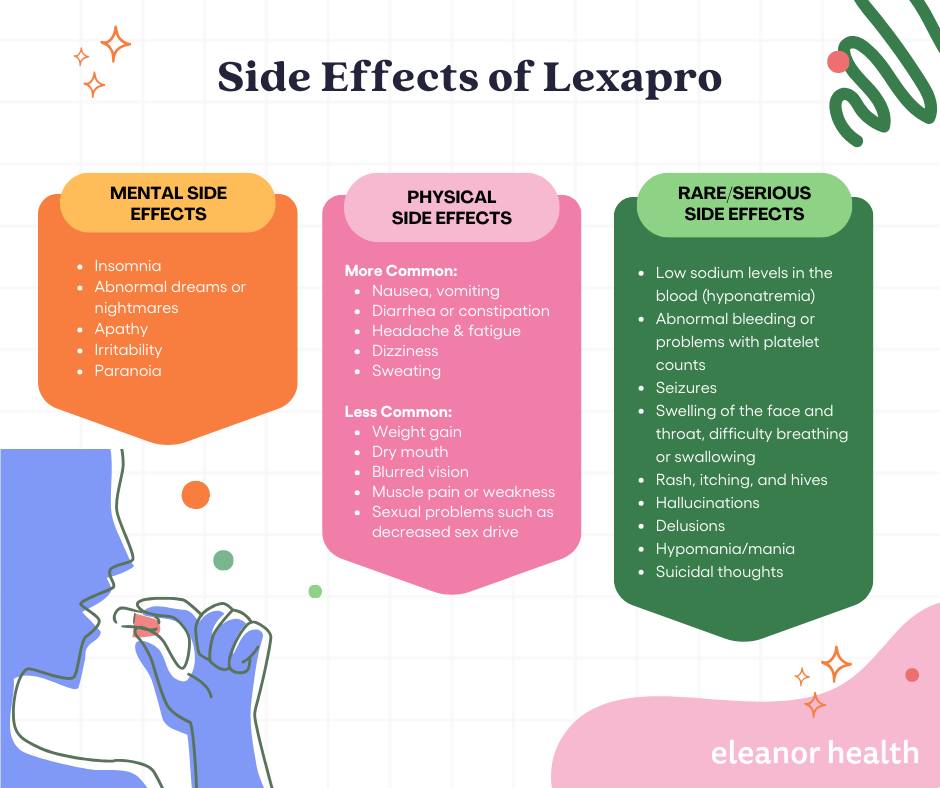
The most common physical side effects associated with Lexapro include:
Less common physical side effects include:
Common emotional and cognitive side effects of Lexapro include:
Although rare, some serious side effects are associated with taking Lexapro. These include:
Additionally, taking Lexapro with certain medications or herbs may increase serotonin activity to dangerous levels, leading to serotonin syndrome. This potentially life-threatening drug reaction can cause muscle twitching, fever, and delirium. If you experience any of the symptoms associated with this condition or any of these serious side effects, contact your doctor immediately.
Lexapro is considered safe for long-term management of anxiety and depression symptoms. However, some individuals may experience new or increased side effects when using the medication over an extended period of time. These can include the following:
It is essential to discuss the possibility of both short and long term side effects of Lexapro with your mental health provider. To note, periods of excessive anxiety and depression also carry short and long term risks to physical and mental health and should be considered when deciding whether or not to use this medication.
As stated previously, serotonin syndrome can develop when mixing Lexapro with other medications that can increase serotonin levels. Below is a list of medications that can lead to this interaction when taken with Lexapro:
Additionally, other medications can interact with Lexapro and should be discussed with a provider before initiating treatment. Some examples include the following:
It’s essential to speak to your provider before starting any new medications or supplements while taking Lexapro.
Most side effects from Lexapro are mild and will usually go away with time. However, there are things you can do to prevent or reduce them.
Communication with your provider is key to managing side effects and optimizing the effectiveness of Lexapro in treating depression and anxiety. Many people don’t report side effects to their doctor, which can affect their experience with the medication and lead to dropping out of treatment. If you experience any physical or emotional side effects while taking Lexapro, the best approach is to discuss it with your provider and work together on any adjustments that need to be made to reduce them.
To reduce risk for or intensity of side effects, you and your provider may choose to initiate treatment at lower doses or adjust when or how the medication is taken. For example, starting treatment at 5mg a day instead of 10mg can lead to better tolerability. Taking Lexapro in the evening may reduce side effects of daytime sedation or fatigue while taking it in the morning can reduce side effects of insomnia. Additionally, taking Lexapro with food can help reduce gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea. It’s important to work with your provider when adjusting the medication as making changes without prescriber consent can significantly impact treatment.
Engaging in lifestyle changes and self-care techniques can help reduce side effects of Lexapro. Examples of self-care include exercising regularly, drinking plenty of water, eating healthfully, getting enough sleep, taking breaks from work or school, and engaging in relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises.
With the potential for mild to moderate side effects, it’s important to know what to expect while taking Lexapro. If you experience any side effects, speak with your provider and work on adjustments together.
Let your provider know if you plan on taking any over-the-counter medications or supplements, as some may interact with Lexapro and raise the risk of side effects.
Lexapro is not typically associated with recreational abuse due to its lack of euphoric effects. However, the medication can be misused in dangerous ways, leading to side effects that range from mild to severe.
Lexapro is misused when people:
Seek medical attention as soon as possible if you’ve taken Lexapro in other ways than prescribed or if you stopped taking your medication without specific guidance from your doctor. Misusing Lexapro can affect both mental and physical health.
Lexapro is designed to be absorbed slowly through the digestive system. Snorting it allows the drug to enter the bloodstream rapidly, leading to high concentrations in the body almost immediately. This can significantly increase the risk of overdose and severe side effects like Serotonin Syndrome. Snorting can also cause significant harm to the nasal passages and respiratory system.
Taking more Lexapro than prescribed can lead to Lexapro overdose. The following severe symptoms after taking Lexapro might point to an overdose:
Lexapro overdose can cause many of the uncomfortable side effects of Lexapro, both mild and serious. In severe cases, Lexapro overdose can be life-threatening. Seek immediate attention if you’ve exceeded your dosage.
Taking Lexapro without a prescription can be dangerous, since there is no professional monitoring of your health and possible interactions. The risk of side effects is much higher, and there is a risk of developing a psychological dependence (Lexapro is not considered physically addictive).
Dealing with anxiety, stress and depression can be very challenging, and there is nothing wrong with taking medication. Sometimes, people struggle with their prescription or take meds they don’t have a prescription for. This leads to very challenging situations. If you find yourself misusing Lexapro, it’s ok to ask for help. At Eleanor Health, we can help you tackle your prescription drug addiction and any co-occurring mental health conditions you might be dealing with.
If you are taking Lexapro and looking to start treatment for a substance use disorder (SUD), you might wonder about possible interactions between your antidepressant and new prescriptions you could get to help you reduce your substance intake.
Lexapro can interact with some medications prescribed as part of medication-assisted treatment for addiction. Lexapro is not known to interact with medications like disulfiram and Acamprosate, which are used to treat alcohol dependence. However, Lexapro can, in rare cases, interact with buprenorphine, one of the few medications used to treat opioid use disorder. The interaction can possibly increase the risk of an irregular heart rhythm. This side effect is relatively rare, but potentially life-threatening.
If you are on Lexapro and want to treat your alcohol or opioid dependence, Eleanor Health can help you find the right approach. We will take into account your current medication and craft a personalized plan that ensures you get the support you need from your prescriptions without putting your health at risk. Reach out today to learn about safe, effective treatment.
While Lexapro takes a few hours to increase serotonin levels in the brain, it usually takes about 4–6 weeks to experience the full benefit of the medication. Some key signs that Lexapro is working include feeling more energetic, worrying less, having fewer negative thoughts, sleeping better, and feeling more hopeful.
If your depression or anxiety symptoms do not improve after six weeks of taking Lexapro, contact your provider to discuss dosage adjustments, changing medication or using adjunctive treatment.
If you miss a dose of Lexapro, take it as soon as you remember. If it’s close to your next dose (within a few hours), skip the missed dose and continue your regular dosing schedule. Do not take two doses at once or take an extra dose to compensate for the missed one.
Not everyone reacts the same way to alcohol when taking Lexapro. The effects of mixing alcohol and Lexapro may depend on the dosage you take and how much you drink. Research suggests that people who take the maximum dosage for depression and anxiety (20mg a day) may have a higher risk for experiencing side effects or complications from drinking alcohol. Finally, drinking while taking psychiatric medication can reduce the efficacy of the medication. Therefore, it’s best to talk to your provider about potential risks and whether or not you should avoid alcohol while taking Lexapro.
 What are SSRIs?
What are SSRIs?
 Therapy for Anxiety, Depression, Trauma: 3 Common Types
Therapy for Anxiety, Depression, Trauma: 3 Common Types
 The Link Between Anxiety and Alcohol
The Link Between Anxiety and Alcohol