In today’s fast-paced world, maintaining good mental and heart health is more important than ever. Heart disease is currently the leading cause of death in the United States, while mental health issues affect tens of millions of Americans each year. Because of the prevalence of these two problems, understanding the connection between them is crucial for anyone interested in their long-term health.
In this article, we’ll go deep on both issues. We’ll explore how mental health affects heart health, the specific mental health issues related to heart disease, as well as what you can do to improve both your mental and heart health.
Mental health plays a significant role in our overall well-being, including our heart health. Research from the Journal of the American Heart Association has shown that people who reported 13 poor mental health days within the past 30 days had a 1.5 times higher odds of heart disease. These odds doubled for those with 14 or more poor mental health days.
While depression and anxiety can be major factors, the most common connection between mental health and heart health involves stress. Prolonged stress can have a negative impact on the heart, increasing the risk of developing heart disease.
Stress isn’t the only way your mental health can impact your heart health, though. Mental health issues can also make it more challenging to maintain a healthy lifestyle, which is essential for keeping our hearts healthy. Individuals experiencing depression or anxiety, for example, may find it difficult to exercise regularly or maintain a balanced diet, both of which are necessary for keeping your heart healthy.
Several mental health issues have been linked to an increased risk of developing heart disease. While we don’t know for certain all the elements at play, research suggests it’s likely a combination of both biological and behavioral factors:
Depression: People with depression are more likely to engage in unhealthy behaviors, such as smoking or physical inactivity. A study published by the American Journal of Medicine points out that there is an 80% increase in the risk of developing or worsening a heart condition, as well as potential death, in adults with depression – whether they had a prior heart issue or not.
Anxiety: The body’s response to anxiety can increase a person’s heart rate and blood pressure. Chronic anxiety that results in increased blood pressure or heart rate may increase the risk of heart disease.
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): PTSD has been associated with a higher risk of heart disease – likely due to the chronic stress and anxiety experienced by individuals living with this condition.
Bipolar disorder: People with bipolar disorder may have an increased risk, potentially due to the high levels of stress and lifestyle factors associated with this condition.
Schizophrenia: Schizophrenia has been linked to a higher risk of heart disease. This is potentially due to factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and high rates of smoking among individuals with this condition.
Substance use disorders: Substance use disorder, particularly alcohol and drug use, can have a detrimental effect on heart health.
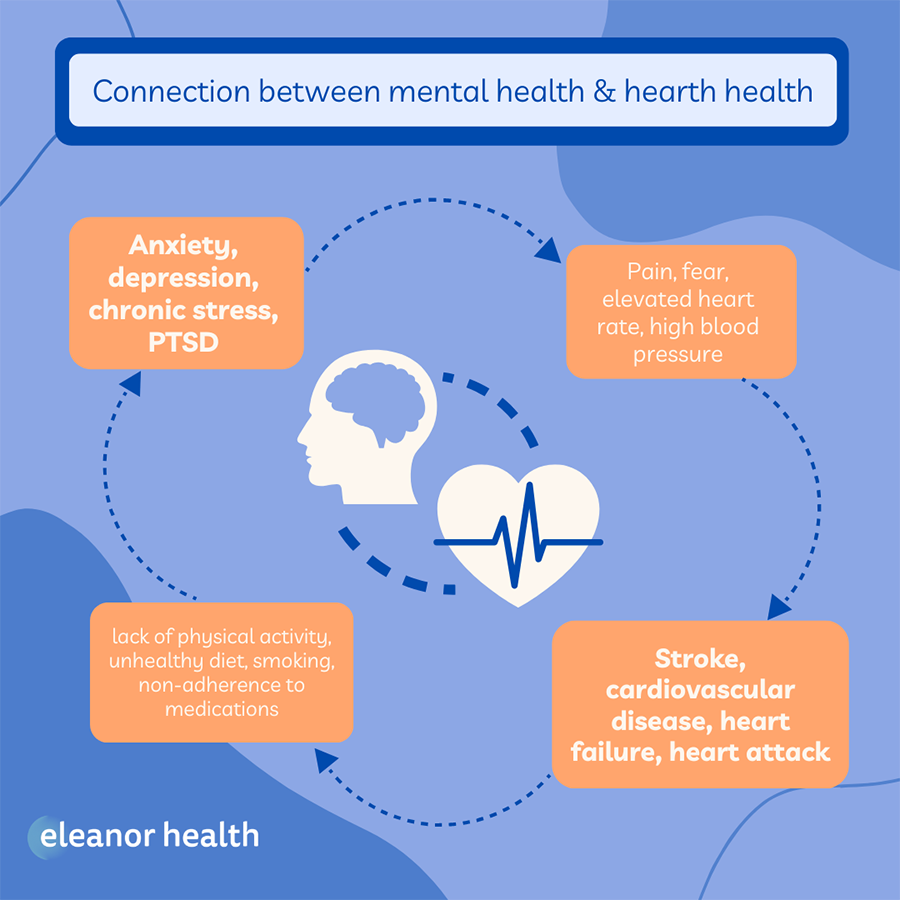
As we’ve mentioned, the relationship between mental health and heart disease is complex, with several risk factors contributing to this connection. A few of the most common ones include:
Unfortunately, individuals with mental health issues are often more likely to have these risk factors, making them more susceptible to developing heart disease. There’s good news here though: By addressing mental health issues, individuals can often see improved heart health as well.
To improve your overall health, consider incorporating the following strategies into your daily routine:
Physical activity is essential for your health. Exercise can help reduce stress, improve mood, and increase the production of endorphins – which are natural mood elevators. Regular exercise strengthens the heart, improves circulation, and reduces the risk of heart disease.
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities twice or more per week.
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats offers a ton of health benefits. These foods support brain function and overall mental health, in addition to lowering the risk of heart disease.
Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds, are particularly beneficial for brain health. Focus on consuming foods high in fiber, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Limit your intake of saturated and trans fats, which can contribute to high cholesterol levels.
Sleep is essential for both mental well-being and heart health. It allows the brain to rest, recover, and process information. It also plays a role in maintaining a healthy heart by regulating blood pressure and inflammation levels.
Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night, and establish a consistent sleep schedule to help regulate your body’s internal clock.
Incorporate relaxation techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga.
These practices can also benefit heart health by reducing your chronic stress, which has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease.
Obesity can increase the risk of both mental health issues and heart disease, as excess weight can lead to high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
To maintain a healthy weight, focus on consuming a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity. If necessary, consider working with a registered dietitian or nutritionist to develop a personalized weight loss plan.
If you’re struggling with your mental health or managing heart-related conditions, don’t hesitate to seek help from healthcare professionals. Early intervention and appropriate treatment can lead to better long-term outcomes.
Smoking is a major risk factor for both mental health issues and heart disease, as it can damage the lining of your arteries, reduce the amount of oxygen in your blood, and negatively impact mental health.
Need help giving up cigarettes? Consider seeking support from a healthcare professional, support group, or smoking cessation program.
High blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes can all contribute to both mental health issues and heart disease if left untreated. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help you monitor and manage these conditions.
In addition to medication, lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management can play a crucial role in controlling these conditions and reducing your risk of health problems.
There is a strong connection between mental health and heart disease, with several mental health issues increasing the risk of developing heart disease. By taking care of the “whole person” and adopting a holistic approach to healthcare, we can promote both mental and heart health, leading to improved overall well-being.
Eleanor Health is here to help you build your confidence and momentum towards the future you want. We can help you manage your mental health and chronic conditions with services like virtual therapy and nurse care management. We are currently located in Florida, Louisiana, Massachusetts, North Carolina, New Jersey, Ohio, Texas, and Washington. Don’t hesitate to reach out for support in your journey towards better mental and heart health.
 What is Whole Person Care?
What is Whole Person Care?
 10 Best Apps for Mental Health
10 Best Apps for Mental Health
 Benefits of Exercise on Mental Health
Benefits of Exercise on Mental Health